HPE
 > Technology > HPE > Virtualization
> Technology > HPE > Virtualization
- Virtualization
- HCI
- VMware

Concept of virtualization
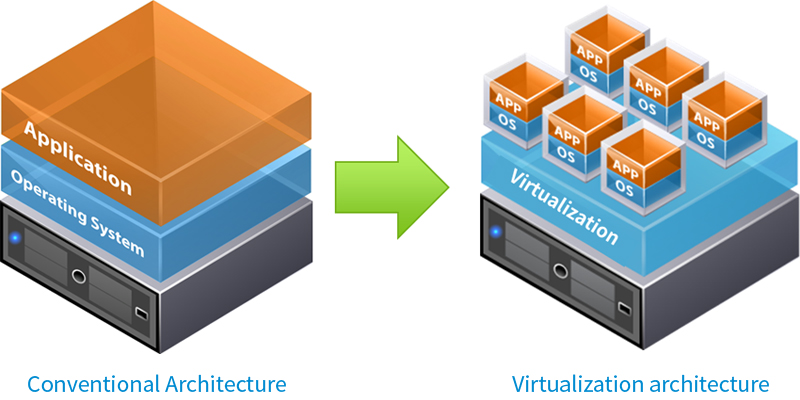
Virtualization is a technology that allows creation of an abstraction (a virtual version) of physical components (e.g. hardware device). With this abstraction, a single machine can act like several machines working independently or multiple machines as a single machine. It is a core technology for cloud computing by providing shared resources for users.
Definition of virtualization
Virtualization is defined as a technique for hiding the physical characteristics of computing resources from the way in which other systems, applications or end users interact with those resources. The commonly used term refers to the followings:
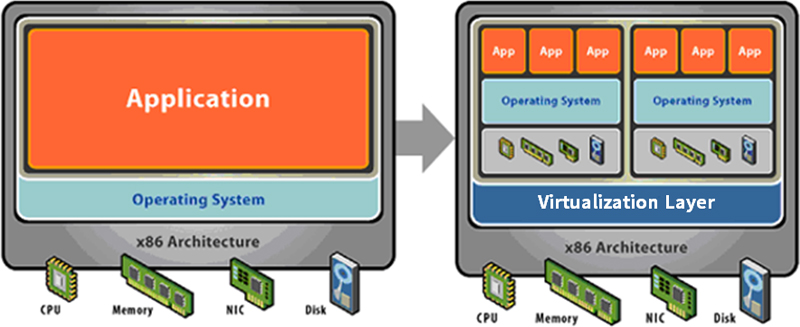
- 1Operating multiple systems on a single physical machine.
- 2Making CPU, memory, HDD and NIC logical using software.
- 3Converting physical server unit to application unit.
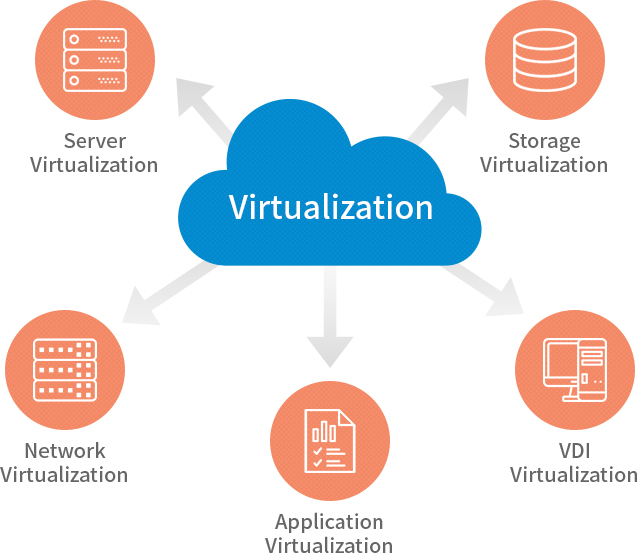
Types of virtualization technology
table
| Types of virtualization technology |
Description |
Application
Virtualization |
- Applications installed separately on the user’s PC Virtualization can be provided through virtualization.
- This enables delivery of applications on-demand without having to install the applications on the PC.
|
Desktop
Virtualization |
- Server-side desktop virtualization enables a user to virtually own dissimilar desktops with different operating programs such as Windows Vista and Windows 7.
- Client-side desktop virtualization makes it possible to operate dissimilar virtual desktops within a PC.
- A separation between personal operating space and company operating space is possible with such method.
|
Server
Virtualization |
- By integrating and consolidating dozens of physical server workloads in a data center into a couple of virtual servers, you can reduce physical overhead costs, administrative costs, and IT energy consumption, and improve the utilization of server resources.
|
Storage
Virtualization |
- A service can be implemented by allocating the minimum space required through virtualization using the technology called “Thin-Provisioning” instead of using physical storage required.
- It also provides an environment for integration of different storage systems.
|
Network
Virtualization |
- It allows you to use L2, L3, L7 switches, network firewalls, and security devices that are available in the form of hardware appliances as virtual machines. Networking resources operate separately even in a single shared physical environment through virtualization.
|
Expected benefits of virtualization
Virtualization technology can improve the utilization of ICT resources in terms of flexibility, security, and scalability while reducing maintenance costs by sharing, pooling, emulating and encapsulating the resources. It also ensures interoperability and protects your investments on the existing systems. To summarize, virtualization lowers a company's TCO(Total Cost of Ownership), increases the flexibility and efficiency of utilizing ICT resources by sharing them.
table
| Classification |
Benefits of virtualization |
Description |
| Lower TCO |
Resource utilization |
- Dynamically share physical resources and resource pool
|
| Maintenance cost |
- Maintenance through automation, informatization and centralization
- Improve productivity of HR through simplification of process
|
More
flexibility |
Flexibility in use |
- Dynamic reconfiguration and utilization of resources in response to fast changing business requirements
|
| Security |
- Provide stable access through separation and isolation
|
Use of
shared
infrastructure |
Availability |
- Ability to change physical resources without affecting users
|
| Scalability |
- Expand virtual resources without having to change physical resources
|
| Interoperability and protection of existing IT investments |
- Enable compatibility at a protocol level and the interface that is not available for physical resources
|
| Provisioning |
- Fast allocation and provision of virtual resources regardless of physical unit of ICT resources
|
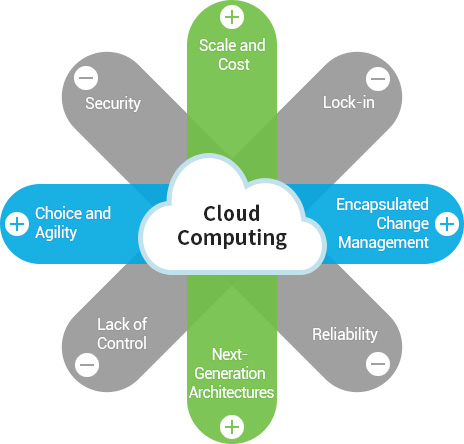
What is cloud service?
A new paradigm that enables the use of more efficient and economical IT environment without having to own various IT resources and functions

- Use IT resources and functions at anytime, anywhere
- Only pay for the amount you have used
- No complex installation process
- Fast scalability
- Measured service
Cloud service allows users to use services without having to purchase IT resources and pay for the service like using electricity as a service.
Cloud computing enables a payment system based on the amount of service used.
Why do we have to use cloud service?
You can use the service at a reasonable price at anytime, anywhere as long as you have internet connection. It also provides safe and flexible working environment for improved productivity.
- 1You can use the service anywhere.
-
As long as you have internet connection,
you can use the service anywhere with the same
environment as your office.
You can work outside your office with a PC,
tablet PC or smart phone.
- 2It is economical.
-
You only have to pay for the service you have used.
It saves you the cost of purchasing, operating
and maintaining IT resources.
- 3It keeps your data safe.
-
Your data is stored in a data center with the advanced disaster prevention technology and uninterrupted systems.
Triple data storage/backup keeps your data safe.
24 hours a day, 7 days a week monitoring system prevents any unauthorized access and hacking.
- 4It improves your productivity.
-
Flexible working environment (e.g. working from home) can improve your productivity.
Outsourcing IT operation and maintenance helps you focus on your core business.
Cloud service models
Cloud computing service models come in three types:
SaaS (Software as a Service),
PaaS(Platform as a Service),
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
Saas
- Software as a Service
-
Provide software as a service for users through internet

Paas
- Platform as a Service
-
Provide platform as a service for system implementation

Iaas
- Infrastructure as a Service
-
Provide IT infrastructure as a service for system and service construction

Cloud service details
IaaS, PaaS, SaaS – Service details
-
-
| Infrastructure |
| Virtualization |
| Automation |
| Management |
| Application |
- IaaS
-
| Infrastructure |
- Scale-out architecture
- Highly integrated computing server
- Storage with high scalability and performance
- Distributed core network for scalability
|
| Virtualization |
- Maximization of resource utilization through virtualization
|
| Automation |
- Definition of cloud platform operation policies and service levels
- Automated resource provisioning
- Self-cloud service
|
| Management |
- Infrastructure usage status and prevention of failure
- Management of cloud infrastructure lifecycle
|
| Application |
- Simplification of operating systems and applications
- Compatibility check for the existing application operation
|
- PaaS
-
| Infrastructure |
- SDN(Software Defined Networking)
- Converged Infrastructure
|
| Virtualization |
- Streamlined development and operation platforms
- Platform for cloud-based application development
|
| Automation |
- Enterprise integrated service delivery platform
- Service orchestration
- Automated service creation for common service infrastructure e.g. WAS, DB
|
| Management |
- Integration of application performance management in development platform
|
| Application |
- Standardization of operating systems and applications
- Modification and redevelopment of application for service reuse
|
- SaaS
-
| Infrastructure |
|
| Virtualization |
- Virtualization architecture with multitenant support
- Integration of service workloads between data centers
|
| Automation |
- Automatic scaling of service workload cluster
- Automated HA and BCP at service workload level
|
| Management |
- Service analysis and reporting
- Metering and payment policy
- Security platform with multitenant support
- Capacity planning support
|
| Application |
- Automated application conversion platform
- Implementation of application with maximized use of SDP
|
Considerations for introducing cloud
The advancement of cloud computing allows companies of any size to optimize their IT investments, achieve economies of scale, reduce costs and drive business innovation
- 1Network traffic
-
Need to build infrastructure that has reliable access to centralized IT resources through network
Need to secure sufficient network bandwidth based on work environment, information system and user environment
- 2Misuse and abuse of centralized information
-
Recommended to establish information management and operation polices in response to misuse and abuse of information
Need to establish and apply access control policy based on the importance of data
- 3Unstable service
-
Service must be planned according to the application service types, characteristics and operation pattern as in the cloud environment, various types of software and solutions share common computing resources
Recommended to set mid- to long-term plans to secure operation strategy and system for cloud-based IT resources
- 4Risk of information leakage
-
Need to build security systems for each service and system (e.g. application, server, network, data) against cyber-attacks and hacking as corporate and personal data is centralized and managed
Classification by service user
- Cloud computing service implemented internally for companies and organizations
- Can be modified for easy use by each company/ organization
- Managed by company/ organization's managers
- Cloud computing service for specific groups
- Access granted only to its members
- Data and application programs are shared among the members
- Public cloud is an essential cloud service model
- Provide resources such as programs and storage devices to several users
- (Examples)
DUZON, Ndrive, DropBox
- Service combining public and private cloud services
- Private cloud service for business data
- Public cloud service for non-business data

Evolution of convergence
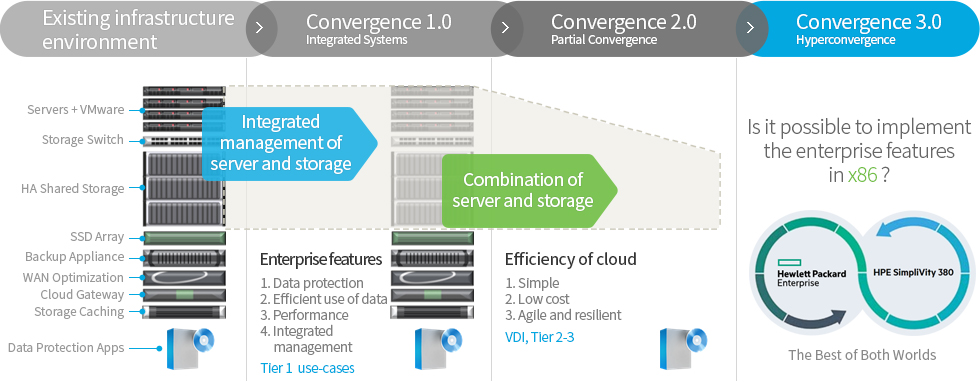
Vision


Service Map
SimpliVity features and benefits
- Guaranteed
date efficiency
-
Always-on compression and deduplication
All data at inception, globally
OmniStack for high performance I/O processing
Guarantee 90% capacity reduction for operation storage and backup
 |
Guaranteed
Data Efficiency |
- Built-in resiliency, backup,
and disaster recovery
-
Full logical backups with almost no overhead
Guarantee 1TB VM disaster recovery within 60 seconds
Accurate RTO/RPO at the level of second to hour
Simple, affordable offsite DR
 |
Built-In Resiliency,
Backup, and
Disaster Recovery |
- Global VM-centric
management and mobility
-
VM-centric policy-based management
No LUNS, shares, or volumes
Right-click operations
Native tool integration
Single view of all data centers and ROBOs
 |
Global VM-Centric
Management and
Mobility |
VMware vCenter
Global integrated management from a single window
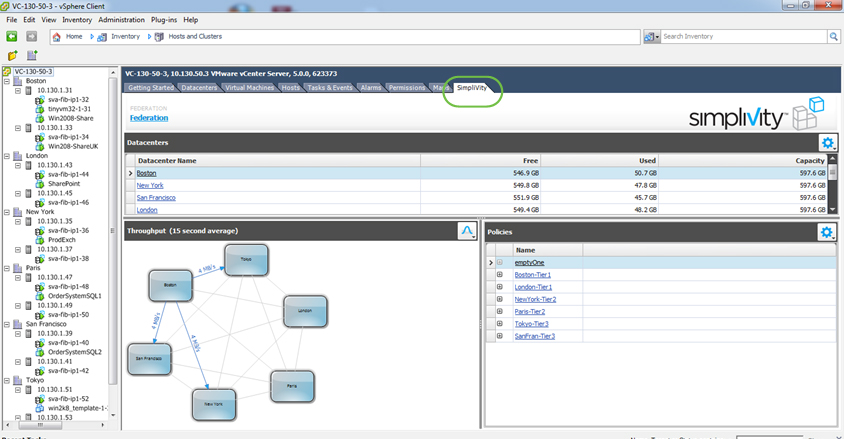
VM-centric work process
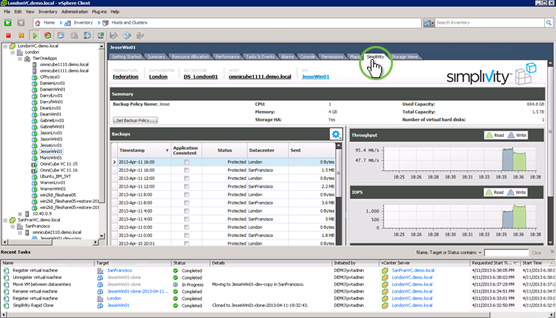
Easy DR protection, recovery and multi-development cloning, and restoration
- VProvide mobility solutions for IO and data by transferring unique data at a VM level
- VM centricity supports all types of task
Backup / Clone / Move / Restore
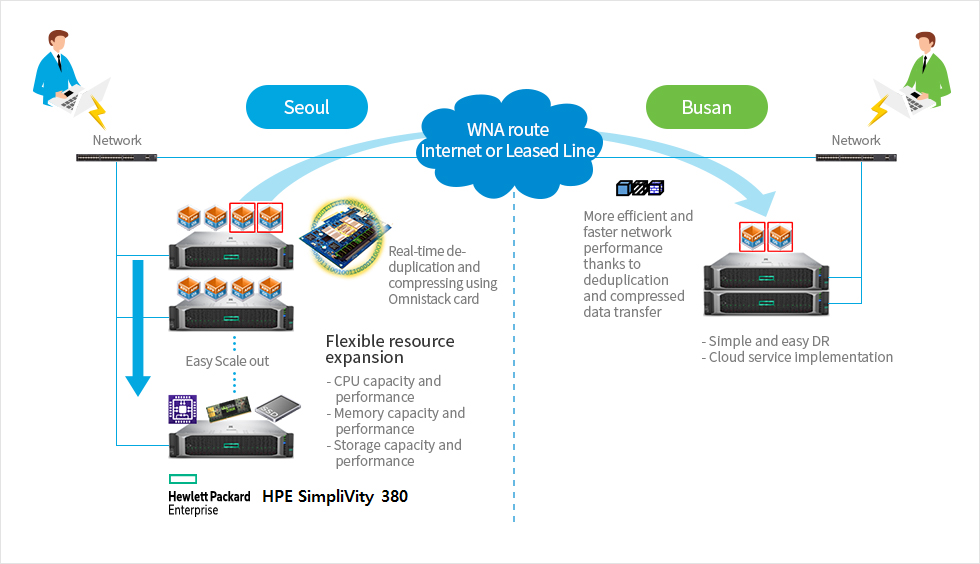
Use Cases

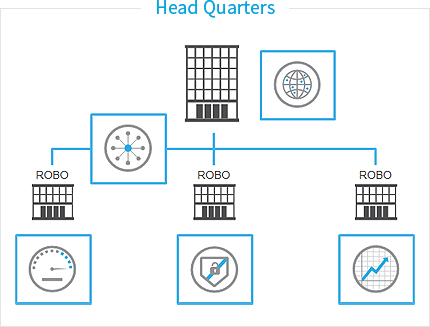
SimpliVity provides integrated and protected ROBO
-
1Consistent application performance
- - Powered by OmniStack card's inline deduplication, compression and optimization
-
2Fast, stable data protection with low risk
- - Protection of essential data
- - Centralized backup policy
- - Transfer of only unique blocks
-
3Maximization of the existing WAN's efficiency and benefits
- - Efficient inline data reduces data transferred via WAN
- - No optimized WAN appliance required
-
4Global integrated management of all ROBOs
- - All resources are managed at central headquarters
- - Easy to expand remote connection configuration
- - VM-centric management and mobility
-
5Sustainable growth and TCO reduction up to 3 times
- - All IT services in ROBO "exists under hypervisor"
- - Significant reduction of data center space, energy and cooling
VDI Performance Highlights
Summary of results running VMware Horizon 6 on SimpliVity
HPE SimpliVity 380

Is your data center slowing down due to its increasing complexity?
With on-premises IT control and governance, HPE SimpliVity 380 offers a high level of agility and cost efficiency of cloud to IT leaders. It also provides powerful hyper-converged solutions that can run some of the most efficient and resilient data centers in the world. This solution is designed to dramatically simplify IT systems by combining infrastructure and advanced data services for virtual workloads with the most popular server platforms on the market.
HPE SimpliVity 380 is a small, scalable 2U rack-mountable building block that provides server, storage, and storage networking services, and can be used on the HPE ProLiant DL380 Server. It also provides a complete set of advanced features that dramatically improve the efficiency, management, protection, and performance of virtual workloads with much less cost and complexity compared to conventional infrastructure stacks.
- New support
-
New support for Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016.
-
HPE SimpliVity 380 for Hyper-V can be managed by the virtual system administrator of Microsoft System Center 2016.
- Features
- Complete hyper-convergence in a fully integrated system
-
HPE SimpliVity 380 combines x86 resources, storage, and storage networking into a single hyper-converged system with advanced features.
-
Simplifies management and offers excellent cost-efficiency and agility.
-
Integrated management improves visibility and control.
-
Faster response to business requirements thanks to fast distribution.
-
Integrate virtual machine and infrastructure workloads to reduce VM(virtual machine) sprawl and over-provisioning.
- High and predictable performance
-
HPE SimpliVity 380 ensures predictability and offers near-linear performance at near-wire speeds while reducing latency with all-flash solutions.
-
Reduce I/O and network traffic through hardware-supported inline deduplication, compression, and optimization.
- On-demand scale-in and scale-out
-
HPE SimpliVity 380 is fully scalable depending on your needs.
-
Each node supports a large amount of fully protected VMs (virtual machines).
-
At both local and remote sites, a set of networked nodes can be managed as a single object.
- Advanced data service
-
HPE SimpliVity 380 significantly reduces capacity usage by offering uninterrupted deduplication and compression.
-
Built-in resiliency, backup, and disaster recovery for data protection.
-
Simplifies operation with policy-based management of VM (virtual machine).

History of VMware that has evolved with virtualization
Gen 1: Client Hypervisor
-
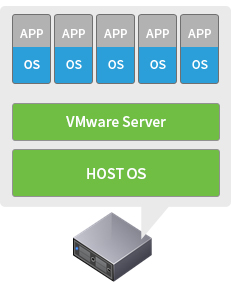
- High usage
- Partial OS/App Fault Isolation
Gen 2: Server Hypervisor
-
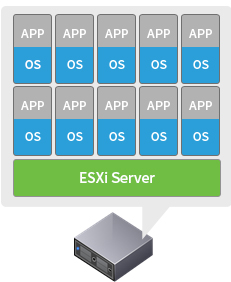
- Full OS/App Fault Isolation
- Encapsulation of VM
- Hardware Independence
Gen 3: Virtual Infra
-
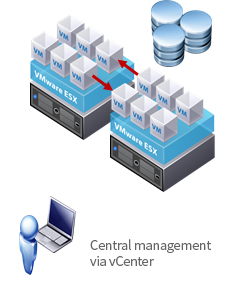
- Centralized management
- Transfer of VM during operation
- Automated business continuity
Gen 4: vSphere
-
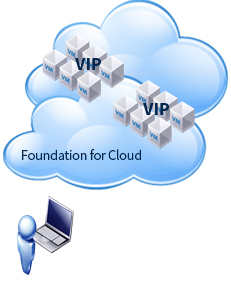
- Policy-based control of Compute, Network, Storage
- (Fault Tolerance) Security and fault tolerance
- Application-centric
Why virtualization?
Increase value of your business through agile IT
-
1
Reduced complexity simplifies operation and maintenance
-
2
Significant reduction of costs means increased investments and more opportunities to create values

-
3
Predict and respond to demands through flexible and agile IT service
Why vSphere?
We took our technology to another level by supporting new and innovative features.
Reduce complexity to simplify
operation and maintenance
-
- Scale-up – SQL Server, Oracle, Exchange,SAP
- Scale-out – Big Data, PaaS, SAP HANA
- OpenStack
- VDI
-

- Remote and inter-local uninterrupted live migration for
- High uninterrupted availability of production VM
- Data protection for business critical applications
Reduce complexity to simplify
operation and maintenance
-

- Simple content sharing and distribution
- Inter-local migration and cloning
- Fast response, intuitive and efficient user interface
vMotion
vMotion
With vSphere vMotion live migration, you can migrate the VM that is running between physical servers without downtime.
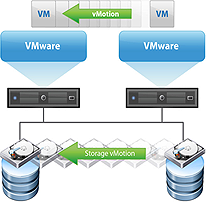
Storage vMotion
Storage vMotion
vSphere Storage vMotion enables live migration of VM's disk files within or to another storage array without service interruption.
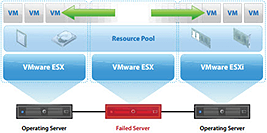
VMware HA (High Availability)
High Availability
vSphere HA (High Availability) monitors VM and its host and provides the foundation for a high availability environment on any operating systems or applications.
Hot Add (Online addition of vCPU and vRAM)
Hot Add
Hot Add allows you to add resources online while running, thus preventing performance degradation or failure due to lack of resources.
- You can hot-add/remove :
-
- · Network cards
- · SCSI adapters
- · Sound cards
- · SCSI disks and CDROMs
- · USB EHCI controller
- · VMCI
- · PCI passthrough devices
Why virtualization?
vSphere Replication (VR) provides the core engine required to configure data protection and DR (disaster recovery) environments for VM, and supports replication for various types of guest OS at no additional cost.
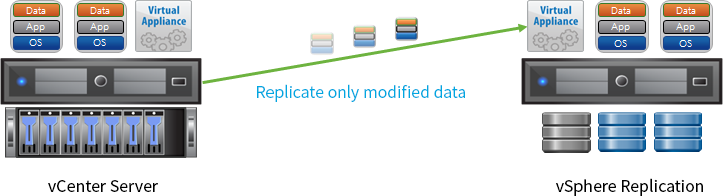
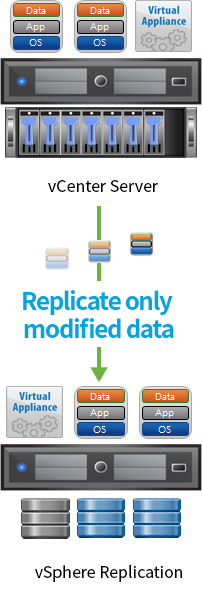
- Features
-
- Built-in VM replication in vSphere enables replication of VM at a host level.
- Replicate only modified data by monitoring VM's I/O in the kernel on ESXi.
- Supports replication at a VM level on any type of guest OS with the function supported by ESXi.
- Support replication on VMware SRM and vCloud Air DR Service.
- Improved features of vSphere Replication
-
- Reduce network bandwidth by transferring compressed data from VM.
- Configure dedicated network for VR traffic, used for replication.
- Improve the reliability of replication by supporting quiescing for Linux Guest OS (Windows Guest OS is already supported).
![]() > Technology > HPE > Virtualization
> Technology > HPE > Virtualization